二维纳米材料(例如石墨烯、二硫化钼等)凭借独特的理化性质,在药物运输、基因转染、组织工程、肿瘤治疗等生物医学领域展示了广阔的应用前景。为了减少体内的聚集,这些二维纳米材料在应用时也需要在表面进一步修饰聚乙二醇(PEG),并且以往的研究也认为这种修饰可以减少巨噬细胞的摄取并增加体内的生物兼容性,所以也被形象地称为PEG的“隐形”效应。
中国科学院过程工程研究所生化工程国家重点实验室生物材料与生物剂型课题组在前期的研究中发现,巨噬细胞与氧化石墨烯的相互作用完全不同于传统球形颗粒(Biomaterials, 2012, 33, 4013; Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 19949)。近期该团队还发现,修饰PEG后的氧化石墨烯(nGO-PEG)虽然不会被巨噬细胞内吞,但却会加速巨噬细胞膜流动性、促进巨噬细胞迁移速率并诱导巨噬细胞产生大量炎症相关细胞因子(图1)。通过与哥伦比亚大学周如鸿教授课题组的合作,该团队进一步发现,nGO-PEG可以借助表面摩擦和嵌插入膜两种方式与巨噬细胞发生相互作用;在此过程中,nGO-PEG会通过刺激细胞膜上整合素αvβ8激活内部信号,最终活化巨噬细胞(图2)。该研究不仅发现了活化巨噬细胞的全新机制,也再次提示二维纳米材料特殊的维度可能引发截然不同的纳米-生物界面效应,在进行生物医学应用时需格外关注。
相关研究内容发表在Nature Communications(8, 14537)上,罗娜娜博士和Jeffrey K. Weber博士为本文的并列第一作者,中科院过程所马光辉研究员、魏炜研究员以及哥伦比亚大学周如鸿教授为通讯作者。该研究得到了国家科技重大专项(2014ZX09102045)、973项目(2013CB531500)等基金的支持。
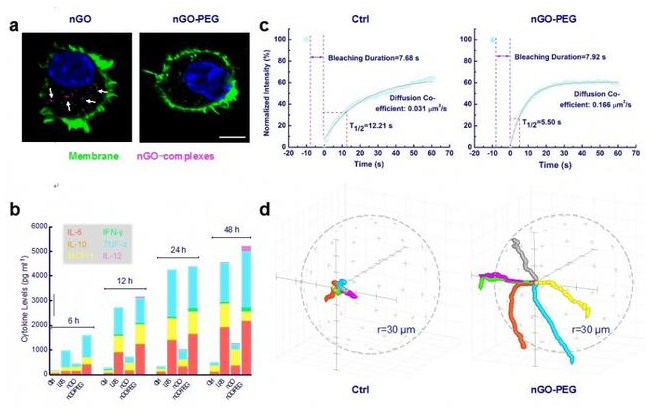
图1 nGO-PEG与巨噬细胞作用后的细胞行为变化:(a)巨噬细胞不吞噬nGO-PEG;(b)巨噬细胞分泌大量炎症相关细胞因子;(c)膜流动性加快;(d)细胞迁移速率增加
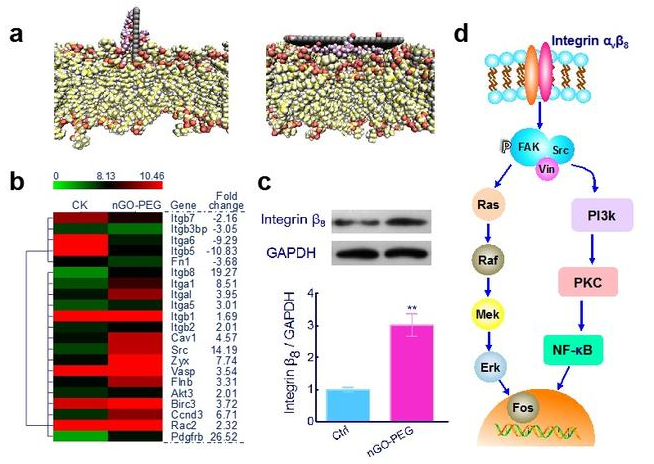
图2 nGO-PEG活化巨噬细胞的机制:(a)计算模拟揭示nGO与细胞膜的两种作用方式;(b)膜相关基因的变化;(c)Integrin β8表达上调;(d)活化通路
原文摘要:
Engineered nanomaterials promise to transform medicine at the bio–nano interface. However, it is important to elucidate how synthetic nanomaterials interact with critical biological systems before such products can be safely utilized in humans. Past evidence suggests that polyethylene glycol-functionalized (PEGylated) nanomaterials are largely biocompatible and elicit less dramatic immune responses than their pristine counterparts. We here report results that contradict these findings. We find that PEGylated graphene oxide nanosheets (nGO-PEGs) stimulate potent cytokine responses in peritoneal macrophages, despite not being internalized. Atomistic molecular dynamics simulations support a mechanism by which nGO-PEGs preferentially adsorb onto and/or partially insert into cell membranes, thereby amplifying interactions with stimulatory surface receptors. Further experiments demonstrate that nGO-PEG indeed provokes cytokine secretion by enhancing integrin β8-related signalling pathways. The present results inform that surface passivation does not always prevent immunological reactions to 2D nanomaterials but also suggest applications for PEGylated nanomaterials wherin immune stimulation is desired.
附件下载: